The Growth & Dominance of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 or Semantic Web (as named by original creator Tim Berners-Lee) is a type of Internet that is based on blockchain technology and operates on token-based economics. Blockchain is a record-keeping system best known for enabling bitcoin transactions. The idea behind Web 3.0 is to create an internet that accurately interprets your input, understands what you convey, and allows complete control over what type of content you want to consume. In addition, web 3.0 promises a more decentralised online experience which means shifting the power back from platform holders (such as Google, Apple, or Facebook) to the customers, and it will establish a network that is open, trustless, and permissionless which makes both users and suppliers participate without authorisation from a governing body.
Web 3.0 theoretically ensures user privacy better, where no organisations or platforms can control your actions on the internet. Decentralised finance, often known as DeFi, is an evolving component of Web 3.0. It requires executing real-world financial dealings on the blockchain without the cooperation of intermediaries like banks or governments.
Meanwhile, with the growing popularity of Web 3.0, many large businesses and venture capital firms are investing money in it, and these funds often split their investment between small and large companies, allowing you to maximise your returns.
Web 3.0 is a potential future internet version based on public Blockchains, a digital ledger or database where encrypted blocks of digital asset data are stored and chained. This is where the entire Bitcoin network relies on.
To further understand, we must first explore the Four key features of Web 3.0
- DECENTRALISATION - blockchain helps to centralize data storage and allows information to be retrieved based on its content. It can be kept in several locations simultaneously, making it decentralized. This would dismantle the vast database currently maintained by internet giants like Facebook, Google, or Apple, giving more control and power over people.
- TRUSTFUL AND PERMISSIONLESS - which means that participants can interact directly without the need for a trusted intermediary or permission from a governing body. For example, you don’t need to accept its cookies or provide any details as there is a trustful bond between you and the web so you can access any data relevant to your choice.
- ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND MACHINE LEARNING - through technology based on semantic web ideas and the nature of language processing, computers can understand this information in the same way that people do.
- CONNECTIVITY AND UBIQUITY – The Internet will be accessible to anyone, anywhere, at anytime
Evolution of the Web 3.0 Technologies
Web 1.0 - it was launched in 1989 and lasted until 2005. The internet was mostly a bunch of static pages, meaning that whenever you loaded, then just showed some stuff, and that was it. Some called it read-only. There wasn’t any logging in or interacting with posts, or viewing analytics.
Most of the early internet wasn't even profitable by ads. It was like one big Wikipedia, all hyperlinked together. Of course, we slowly made improvements with time, and things like flash and JavaScript added many new features. However, during this time, the majority of participants were content consumers, whereas the creators were mostly web developers who produced websites with the information given predominantly in text or visual format.
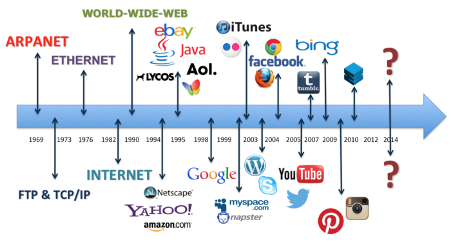
Source: http://ahmadfaizar.blogspot.com/p/evolution-of-web-web-10-web-20-web-30.html
Web 2.0 - From around 2004 until now. During this time, the web evolved a lot, but one of the biggest changes was the interactivity of the Internet.
This meant that not only did we get information from pages, but we could generate ideas and share them with the rest of the world.
In Web 2.0, you can also upload a video and make it accessible for millions of people to view, engage with, and comment on. Web 2.0 apps include YouTube, Facebook, Flickr, Instagram, Twitter, and other social media platforms. These centralised companies started collecting data about us to serve us better content, which would make us stay on their websites longer.
Web 2.0 is the age of targeted advertising and the lack of privacy for its user. You have no control over your data or how it is kept. In reality, corporations regularly monitor and retain user data without their knowledge or consent. All this data is owned and managed by the companies in charge of these platforms. Furthermore, when governments feel someone is expressing a viewpoint that opposes their propaganda, servers are routinely taken down, or bank accounts are seized. Governments may easily intervene, control, or shut down programs using centralised servers.
The Internet was dark primarily and anonymous until the introduction of Friendster, MySpace, and, subsequently, Facebook in 2004. These social networks persuaded users to do certain activities and create content, such as recommendations and referrals - from encouraging us to post images online with specific friend groups to entrusting our homes to unknown tourists on Airbnb and even stepping into a stranger's vehicle with Uber.

Source: https://thinkspace.csu.edu.au/inf330aforbes2016/2018/03/19/what-is-web-2-0/
John Markoff, a New York Times reporter, coined the phrase web 3.0 in 2006. The advent of blockchain technologies brings the third era of the web, the so-called Web 3.0. It is the next evolution of the internet and is based on decentralisation, without points of control and unique profit centres. The blockchain enables the transfer of value without a profit centre or monopolistic service providers. While the advent of social media allowed the exchange of information among users but kept the control among a few private actors (generating digital oligarchy with social media companies, peer-to-peer ridesharing, and peer-to-peer hospitality networks), blockchain technologies allow the possibility of creating decentralised networks without centralised points of control. From this stem, one of the disruptive aspects of this technology will enable it to operate on a decentralised system without any central centre of profit in charge of coordinating (and taking advantage of) the network. Blockchain technology allows the secure transfer of information, assets, and money without a third-party intermediary, such as banks or other financial institutions.
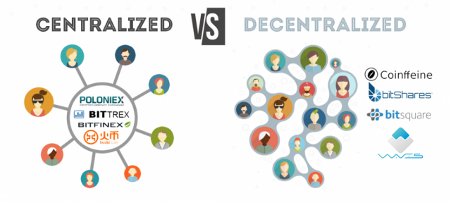
Source: https://www.ukessays.com/essays/politics/centralization-and-decentralization-advantages-and-disadvantages.php
Web 3.0 Architecture
The architecture of web 3.0 is essentially comprised of four elements:
- Ethereum Blockchain - Ethereum is a programmable blockchain that finds application in numerous areas, including DeFi, NFTs, and Smart contracts. It can be used for sending and receiving value globally with its native cryptocurrency, "ether", without the interference of third parties. Essentially, it is owned jointly by everyone, and anyone in the world may access and write to the state machine, but they can never change old data.
- Smart Contracts - are simply programs stored on a blockchain that run when predetermined conditions are met. It is a self-executing agreement where code algorithms specify the terms and conditions. Blockchain developers build these in high-level programming languages such as Solidity or Vyper to specify the logic underlying the state changes.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) — This virtual machine is where all Ethereum accounts and smart contracts are stored. It's accountable for executing the logic expressed in smart contracts. They handle the state changes that occur on the state machine.
- Front End — Like any other program, the front end defines the User Interface logic. It has three essential UI elements - Firstly, the Interactive Design, converts passive readers into active readers where they are allowed to input information. Secondly, Information Architecture, structuring the presentation logically for users to follow along and understand your conclusion and to make it easier for them to navigate the web page. Lastly, in Visual Design, several aspects such as colours, style, images, animations, tables, graphs, and so much more must be considered aesthetically pleasing.
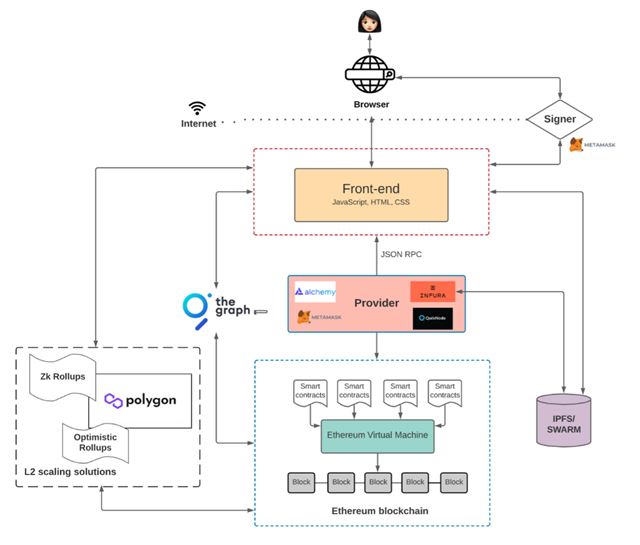
Source: https://www.preethikasireddy.com/post/the-architecture-of-a-web-3-0-application
The benefits of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 will make the web more intelligent, more secure, and more transparent, resulting in more efficient surfing and more effective machine-human interaction.
Here are the top benefits of the semantic web, often known as web 3.0:
- Users will have full ownership of their data and have the security of encryption. Information could then be shared on a permission/need or case-by-case basis. You will be able to pick what information you want to share with businesses and advertising agencies, and you will be able to profit from it. Big tech companies like Facebook, Apple, and Google will no longer be in control of user data.
- Decentralised data storage ensures that users may access their data in any situation. Thus, the users will not need to think about suspending a particular account or service disruptions due to technical or other reasons.
- Users may build their addresses and participate in the blockchain network since it is open to anyone. This network does not allow users to be limited based on gender, income, geographical area, or social characteristics. This function will enable customers to move their assets or riches anywhere in the globe quickly.
The Disadvantages of Web 3.0
There are also several difficulties linked to the adoption of web 3.0. Personal data management and reputation management will be more important than ever.
The following are the most significant problems related to the deployment and use of web3:
- Web 1.0 Websites Will Be Extinct If web 3.0 becomes a full-fledged Internet standard, all websites built using web 1.0 technology would be rendered obsolete. This is because the old technology cannot be updated to meet the new features. This implies that such sites will be obsolete and, as a result, will lose a competitive advantage over new ones.
- It will be inaccessible to less advanced devices, and it will need above-average specifications to use Web 3.0.
- For every new user, the complexity of web 3.0 is likely to limit its extensive adoption. It combines older-generation online tools with cutting-edge technology such as AI and blockchain. As a result, only sophisticated devices can handle web 3.0, making it impossible for any person or organisation that cannot buy such devices.
Conclusion
Web3 is currently a work in progress and is not precisely defined yet. However, it is full of incredible possibilities but comes with some risks. The main principle of Web 3.0 is Decentralisation, rather than being controlled by intermediaries. Therefore, it has many advantages with the prospect of enhancing how we interrelate with the web.
References
What Is Web3? Potential of Web 3.0 (Token Economy, Smart Contracts, DApps, NFTs, Blockchains, GameFi, DeFi, Decentralized Web, Binance, Metaverse Projects, Web3.0 Metaverse, Crypto guide, Axie) By Patrick Ejeke
(Routledge Studies in Science, Technology and Society (Book 41)) Massimo Ragnedda (editor), Giuseppe Destefanis (editor) - Blockchain and Web 3.0_ Social, Economic, and Technological Challenges (Routl).